About outputting to a file
When you select the
Overwrite Existing Files with Same Name
check
box, in the
Processed File Options
section of output process templates,
the old file is overwritten in all cases.
When the
Overwrite Existing Files with Same Name
check box is
cleared, the file naming scheme described below is used.
When you output a file the second time, the older file is renamed with
the addition of a version number, and the new file takes on the original
name of the first file. Subsequent output causes the version numbers of
all old files to be incremented by one number (to a maximum of nine
old versions). The effect of this constant renaming is that, regardless of
the number of times you output the same information in the same way,
the most recent file is always named the same and the oldest file
contains the highest version number.
Examples
In the following examples:
●
1A
is the signature and surface number (for loose page output this
is always 1A) .
●
C
is the color (CMYK for composite; GRAY for grayscale; and one of
C, M, Y, or K for a separation).
●
<ext>
is the appropriate three-character extension for the file type,
for example, .JPG, .VPS, .TIF.
●
.1.
is the version number (up to a maximum of .9).
●
* indicates the oldest file.
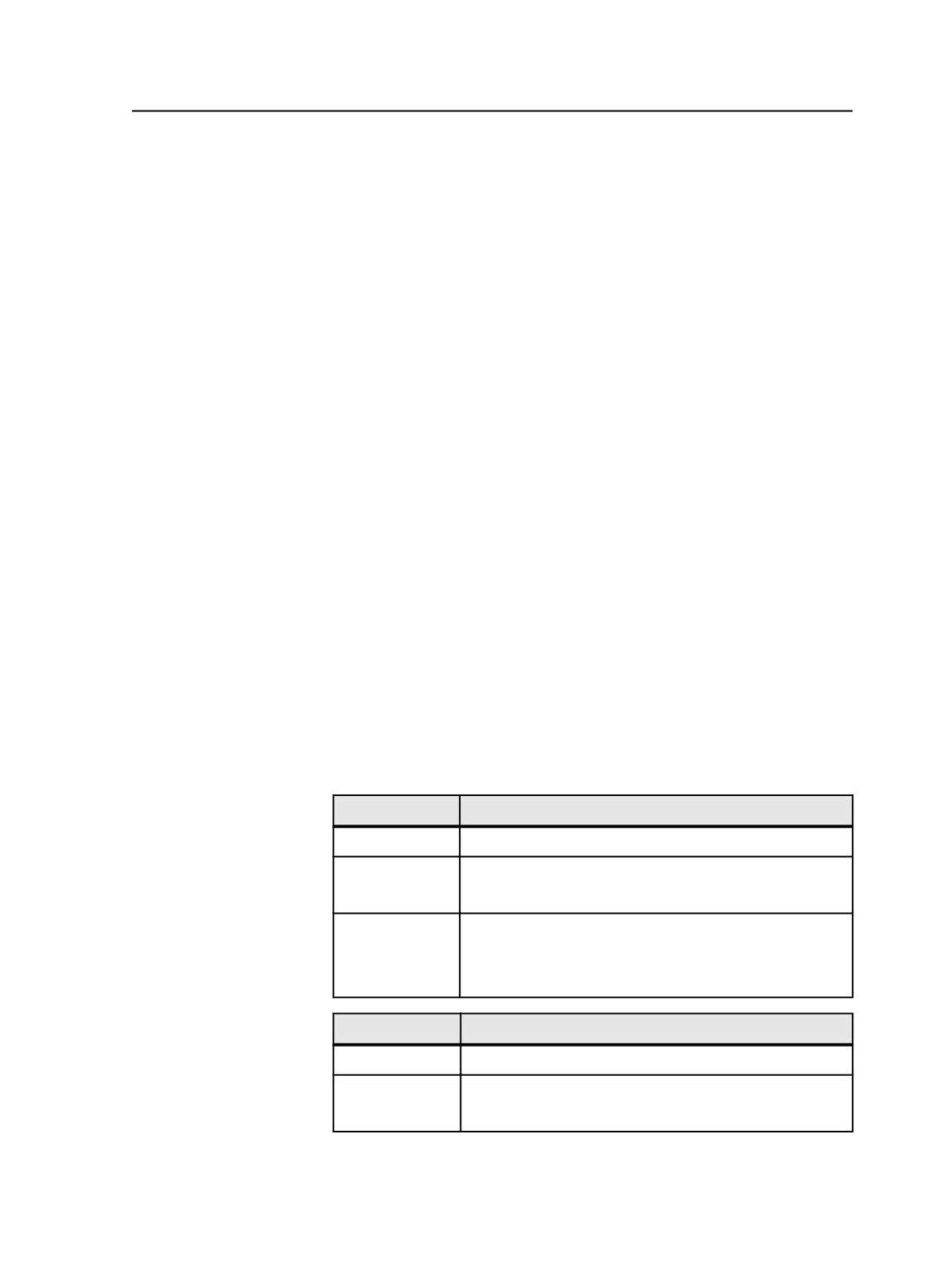
Output #
Loose Page Results
First
<page name>.1A.C.<ext>
Second
<page name>.1A.C.<ext>
<page name>.1A.1.C.<ext>*
Third
<page name>.1A.C.<ext>
<page name>.1A.1.C.<ext>
<page name>.1A.2.C.<ext>*
Output #
Imposition or Final Results
First
<job name>.1A.C.<ext>
Second
<job name>.1A.C.<ext>
<job name>.1A.1.C.<ext>*
About outputting to a file
661


