Available if the
Center Along Height
check box is cleared.
Shifts the imposition plan from the bottom edge of the media
along the vertical axis.
Scale Shift Amounts
Automatically adjusts placement based on scaling.
If the
Scale Shift Amounts
check box is cleared, placement is
not adjusted when scaling is applied.
By default the
Scale Shift Amounts
check box is selected.
Flat Rotation
Makes a small angle rotation of the flat or output image. Also
called plate cocking. Derive the
(0.0)
percentage value, or
gradient, in one of two ways:
●
Physically measure the first occurrence of a rotation to find
the gradient that you can then apply for all jobs that use that
rotation
●
Convert a given angle into its gradient
To measure for a gradient:
●
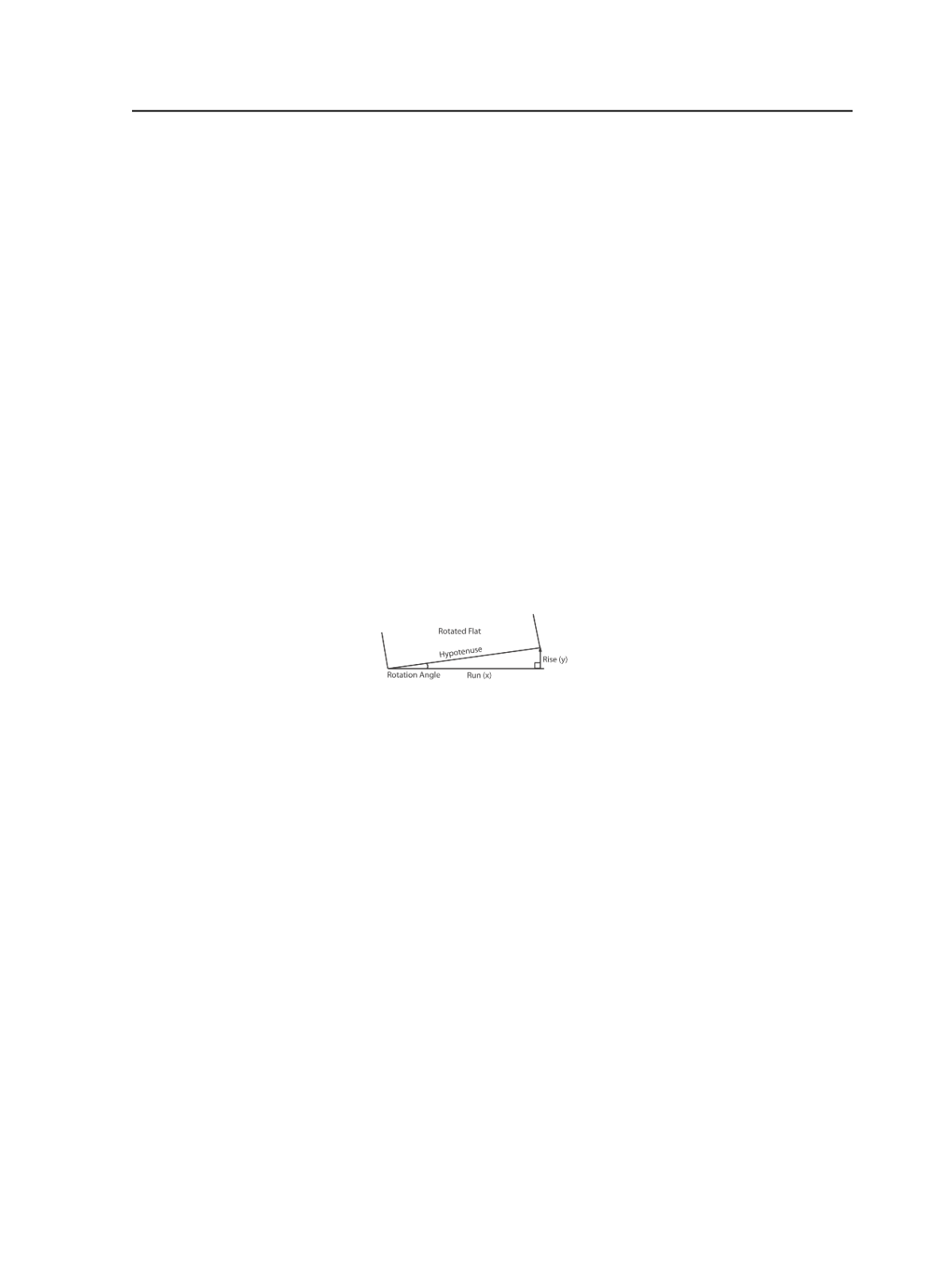
Formula: gradient = rise/run x 100 where:
●
Rise: (y-axis) measure the distance between where the flat's
rotating corner started and where it must be moved as a
straight line that meets the x-axis at a 90° angle. Example: 2
units
●
Run: (x-axis) measure the distance along the x-axis from the
non-rotated corner of the flat to the point where the vertical
line transects the x-axis at a right angle. Example: 90 units
●
Calculation: 2/90 x 100 = 2.2
●
The maximum percentage value is 3.1.
To convert an angle to a gradient:
●
Formula: gradient = tangent of the angle of rotation x 100
●
Calculation using a scientific calculator and an angle of 0.5°:
●
0.5° + Tan(gent) key = 0.008 x 100 = 0.8
●
The maximum angle of rotation is 1.78°.
Note: To convert a gradient to an angle, enter the gradient into the
calculator and apply the inverse tangent function. Example: 2.2% is
entered as 0.022 + Inv(erse) key + Tan key = 1.26°.
Final Output process template
559


